INTRODUCTION SHADE
CARDS
HE
dyes are suitable for dyeing cotton and other cellulosic materials. Tese dyes
possess significantly higher exhaustion and fixation efficiency which
results in appreciable cost reduction in comparison to convectional reactive
dyes. The high fixation and good build up are of particular importance
when dyeing polyester/ cellulosic blends where liquor : goods ratio is
quite high. Due to higher fixation of HE dyes, the drained and wash liquors
after dyeing contain much less quantity of unmixed dyes, i comparison
to conventional reactive dyes, which is of interset when pollution control
is a major concern to everybody. This facilitates quicker wash off and efficient
soaping. The improved stability of HE dyes gives improved batch to batch
consistancy. Exhaustion of HE dyes can be controlled by salt addition
and temperature to give level dyeing before alkali addition.
The other useful features of HE dyes are as under :
1. Excellent
build-up in high as well as low liquor : goods ratios.
2. The high fixation is of particular importance when
dyeing polyester/cellulose blend when liquor/ goods ratio is
quite high. Under the circumstances, conventional
reactive dyes show low dyeing efficiency and poor build-up.
3. Excellent reproducibility.
4. Wide applicability on yarn, piece material, loose
stock and garments.
5. Wide choice of equipment to suit a particular application.
Dyeing
Methods
Winch,
jet, package & Beam dyeing machines.
These dyes are specially designed for exhaust dyeing methods. The dyeing
method selection depends upon the type of substrate to be dyed and the
machinery to be used for dyeing.
|
Depth of shade |
Salt |
|||
|
(gm/l) |
Mercerised |
Soda
Ash |
Fixation
time |
|
|
Upto 0.1% |
10 |
5 |
10 |
30 |
|
0.11-0.30% |
20 |
10 |
10 |
30 |
|
0.31-0.50% |
30 |
20 |
10 |
45 |
|
0.51-1.0% |
45 |
30 |
15 |
45 |
|
1.01-2.0% |
60 |
40 |
15 |
45 |
|
2.01-4.0% |
70 |
55 |
20 |
60 |
|
Above 4.0% |
90 |
65 |
20 |
60 |
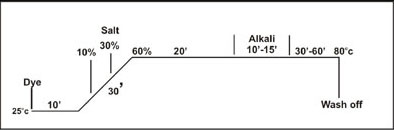
Method No. 1 :
Salt
addition in portions (Suitable for mercerised yarn)
This
process is recommended for non-circulating liquor machinery and it is suitable
for all depths of shade.

Method No. 2 :
Salt
addition at start (Suitable for unmercerised yarn)
This
method is recommended for machines with liquor circulation and it is suitable
for medium to heavy depth of shades.
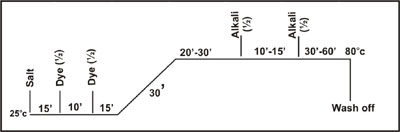
Method No. 3 :
Both
salt and alkali additionat start.
This
method is recommended for machines with liquor circulation, primarily for the
dyeing of medium - heavy binary combinations. It is suitable for unmercerised
cotton.
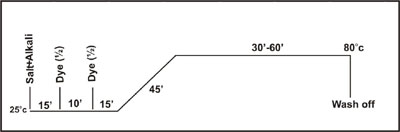
Method No. 4 :
(Dyeing
Pale Shades) (Garment
Dyeing)
This method is recommended for machines with microprocessor controlled
addition system for dyeing pale shades(less than 0.5% depth) and for all
shades on mercerised cotton & viscose packages.
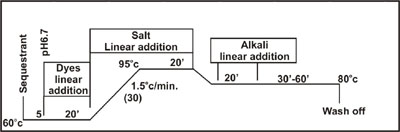
Methods No. 5 :
Isothermal
Method (Dyeing Heavy Shades Garment)
This
method is recommended for machines with microprocessor controlled addition systems
for medium to heavy depths (> than 0.5% depth) on unmercerised cotton.
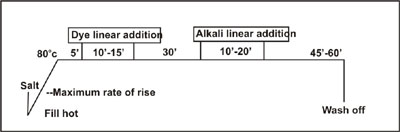
Dyeing
method for jigger machines
Due
to high temperature dyeing, the problems of off-shade selvedges or too pale
selvedges are often
encountered in dyeing with these machines. The following precautions hence
should be taken to avoid such
problems.
1) To use closed type jiggers so that a uniform temperature is possible
accross the width of fabric.
2) Batch the fabric evenly.
3) Maintain the dye bath at minimum of 85-90oC during salt stage.
4) Adjust the dye bath temperature to 85-90oC to ensure that fabric is
maintained at minimum 80oC during alkali addition stage.
Procedure
Set the dye bath at 90oC with resist salt 2 gms/l. Now add 1/2 amt.
of dye and run one end. Then add remaining 1/2 amt.& run an another
end. Maintain 80oC temp. continue to run for 2 ends. Now add 1/2 amount of soda
ash & run for another one end. Then add remaining 1/2 amount of soda
ash & run for another one end. Then run for
4 ends or more if required & wash. (1 end = 10 minutes) Dyeing Methods
for cotton / polyester Blend.
The one bath two stage dyeing method for polyester / cotton blend is applicable
on jet, beam or package dyeing
machines.
2
gm/l Buffer pH 5 (5.5) X%
KALPACTIVE 'HE' dye
1 gm/l Anionic dispersant 40
gms/salt
X% Disperse Dye 15
gms/l T.S.P. or soda ash
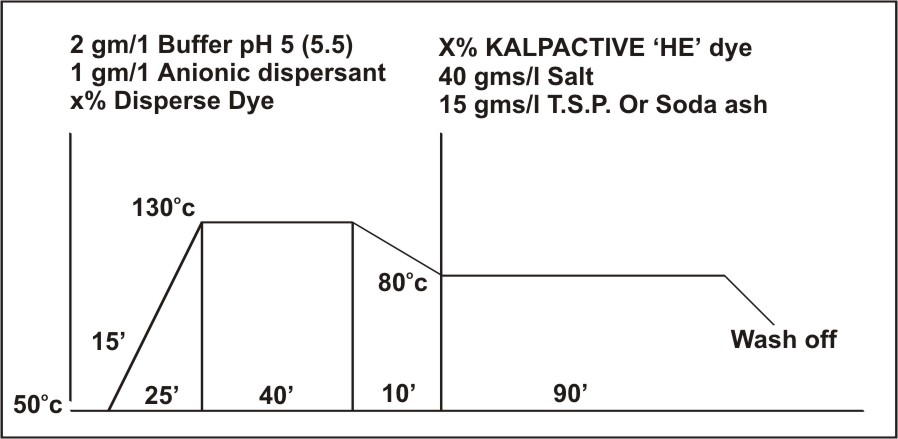
Salt and alkali requirements
|
Depth
of shades % on total |
Salt
|
Soda
Ash |
|
Upto 0.2% |
15 |
10 |
|
0.21-0.4% |
20 |
15 |
|
0.41-0.80% |
30 |
15 |
|
0.81-1.6% |
50 |
20 |
|
Above 1.6% |
70 |
20 |
Washing-off
procedure
In
order to obtain maximum wet-fastness properties, brightness and purity of shades
with consistent dyeing results,
it is essential to give a thorough 'soaping' to clear-off unreacted hydrolysed
dye from the dyed fabric.
The dyed fabric is rinsed repeatedly in cold water to remove most of the
alkali, salt and unfixed dye present and rinse again in warm water not
higher than 60oC. Then run in a bath containing:
Anionic
detergent
1-2
gms/litre for 15 minutes at the boil. Then rinse in warm water (up to 60oC)
and finally in cold water. The satisfactory results in washing-off, particularly
for piece goods, are obtained by employing an open soaper or perforated
Beam-washing machine. If such equipments are not available, conventional ones
like jig or winch may be used. For yarn in the hank from open-vat is employed
and for yarn in packaged from the package-dyeing machine itself used.
| Key to Abbreviations : | |
| L = Low | |
| M = Medium | |
| H = High | |
|
V =Very High |
|
| + =Suitable | |
| (+) = Fairly Suitable | |
| - = Not Suitable |
Dischargeability : G = Good, F = Fair, P = Poor
Light : 1 to 8 in increasing order
Washing & other : 1 to 5 in increasing order
Y = Yellow
O = Orange
R = Red
V = Violet
B = Blue
Br = Brown
Bl = Black
G = Green