(COLD BRAND-DICHLORO TRIAZINE BASED) SHADE CARDS
INTRODUCTION
This pattern card illustrates - dyes in the dyeing of all cotton mercerized poplin. The dyes are of particular interest in the dyeing and printing of cellulosic fibres, such as Cotton, Linen, Viscose, Cuprammonium and Polynosic rayons."c"brands are highly reactive requiring comparatively milder conditions in dye fixation. They are primarly of dyeing at normal room temperature (about25-35o c) using Soda Ash or Sodium Bicarbonate. 'C' Reactive dyes are applicable to cellulosic textiles byBatch-wise, Semi-continuous and Continuous methods in conventional textile machinery like Open-vat, Package, jet, Jig,Winch and Padding mangle.The versatility in various application procedures and the availability of a wide range of bright and fast shades are the outstanding features of this class of dyestuffs.
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF 'C' DYES
Stability
The dyestuffs should be stored in cold and dry conditions. Thecontainers should be tightly closed when not in use. High temperature, humidity and alkaline pH conditions reduce the stability of the dyes in solution. Water Supply Soft or softened water should be employed, avoiding alkalinity especially while dissolving the dyes. When had water alone is available, it should be softened with sequestering agents. In dyeing,the pH of the water supply should be within the limits of pH=7-8.
PREPARATION OF THE GOODS FOR DYEING
In order to obtain satisfactory results, the preparation of the cotton material, prior to dyeing is most important. The goods should be de-sized and scoured well in order to impart adequate absorbency to the substrate and remove all impurities that may impede proper dye uptake in the subsequent dyeing process. Level shades with optimum dye peneterating and colourfastness are obtained only on well-prepared material.
DISSOLVING OF DYESTUFF
The dyestuff is made in to a smooth paste with cold water and dissolved by adding warm water, while stirring. Where solubility limits are exceeded satisfactory solution can be obtained by adding of urea.
DETAILS OF DYEING (EXHAUST METHOD)
This is recommended for cotton yarn in Open-vat (Beck) or Package-dyeing machines: cotton piece goods on Jigger, Winch, Jet-dyeing machines etc. The bath is set at room temperature (about 25-35oc) with pre-dissolved dye and run for 10 minutes. Pre-dissolved salt (Glauber's Salt or Common salt)is added and run for 20-30 minutes.Pre-dissolved alkali(Soda Ash)is then added and dyeing is continued for 30-60 minutes.Finally,Washing-off as described at the end.
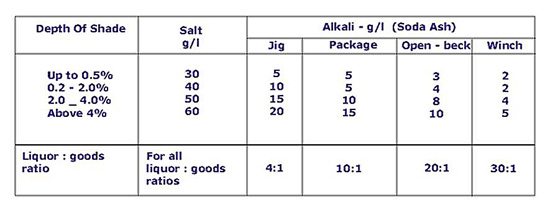
SALT & ALKALI REQUIREMENT: Table 1
SEMI-CONTINUOUS AND CONTINUOUS METHODS OF APPLICATION FOR COTTON PIECE GOODS
In all above methods of application which involve padding, the following precautions are valuable to help avoid "tailing or ending" effects in the dyeings:
a) Employing a small pad trough 'V' or 'U' shaped, having an optimum capacity of 5-10 litres.
b) Using high running speeds commensurate with the needs of the rest of the process and setting the padding mangle to give adequate squeeze. Normally, 60-70% nipexpressin may be kept for cotton goods. The mangle squeeze should be even on the padded goods and the trough, fed with dye liquor to a constant level throughout.
c) In all dye-fixing operations, involving steaming in particular, addition of Resist Salt is recommended to the padding liquor to counteract any adverse reducive action of the dye.
Add 5-10 parts sodium bicarbonate (predissolved) and 2-5parts Calsolene Oil HS to dye padding solution at 20- 30oc. Migration during drying can be minimized by using suitable wetting agent and 10 parts of dissolved common salt or Glauber's Salt (unhydrous) Pad to give minimum pick up. Diffuse into viscose rayon is aided by batching and storing for 1 hour or more before drying. Dry at 100-200oc for 1-2 minutes in hot flue, or pin stenter or on cylinders set to dry slowly. Wash to clear agents and unfixed dye.
Pad-batch method
Pad Liquor composition:
'C' dyes - X parts
Wetting agent - 2-5 parts
Urea(wherever necessary) - 50-200
Soda
Ash -
As per table 1
--------------------------
Total - 1000 parts
Process Dissolve dye, urea and wetting agent. The dye solution and alkali are mixed just before padding. The goods are padded in the above pad liquor solution and immediately batched on plastic sheet and kept for 2 hours and then washed.
Washing-off procedure
In order to obtain maximum wet-fastness properties, brightness and purity of shades with consistent dyeing results,it is essential to give a thorough 'Soaping'toclear-off unreacted hydrolysed dye from the dyed fabric.
The dyed fabric is rinsed repeatedlyin cold water to remove most of the alkali,salt and unfixed dye present and rinsed again in warm water not higher than 60o c.Then run in a bath containing:
Anionic
detergent
1-2 gms/litre for 15 minutes at the boil. Then rinse in warm water (up to 60o c) and finally in cold water. The most Satisfactory results in Washing-off, particularly forpiece goods, are obtained by employing an Opensoaper or perforated Beam-washing machine. If such equipments are not available, conventional ones like Jig or Winch may be used. For yarn in the hank form, open-vat is employed and for yarn in package form the package-dyeing machine itself is used.
| Key to Abbreviations : | |
| L = Low | |
| M = Medium | |
| H = High | |
|
V =Very High |
|
| + =Suitable | |
| (+) = Fairly Suitable | |
| - = Not Suitable |
Dischargeability : G = Good, F = Fair, P = Poor
Light : 1 to 8 in increasing order
Washing & other : 1 to 5 in increasing order
Y = Yellow
O = Orange
R = Red
V = Violet
B = Blue
Br = Brown
Bl = Black
G = Green